Interpreting Graphics
TEAS Test – Interpreting Graphics
In the previous lesson you learned about standards of measure, now this lesson provides TEAS math practice by discussing how to create a bar, line, and circle graph and how to interpret data from these graphs. It also explores how to calculate and interpret the measures of central tendency.
TEAS Test – Creating a Line, Bar, and Circle Graph
A line graph is a graph with points connected by segments that examines changes over time. The horizontal axis contains the independent variable (the input value), which is usually time. The vertical axis contains the dependent variable (the output value), which is an item that measures a quantity. A line graph will have a title and an appropriate scale to display the data. The graph can include more than one line.
A bar graph uses rectangular horizontal or vertical bars to display information. A bar graph has categories on the horizontal axis and the quantity on the vertical axis. Bar graphs need a title and an appropriate scale for the frequency. The graph can include more than one bar.

A circle graph is a circular chart that is divided into parts, and each part shows the relative size of the value. To create a circle graph, find the total number, and divide each part by the total to find the percentage. Then, to find the part of the circle, multiply each percent by 360°. Draw each part of the circle and create a title.


Be Careful
Make sure to use the appropriate scale for each type of graph.
Creating Line, Bar, and Circle Graphs Review
TEAS Test – Interpreting and Evaluating Line, Bar, and Circle Graphs
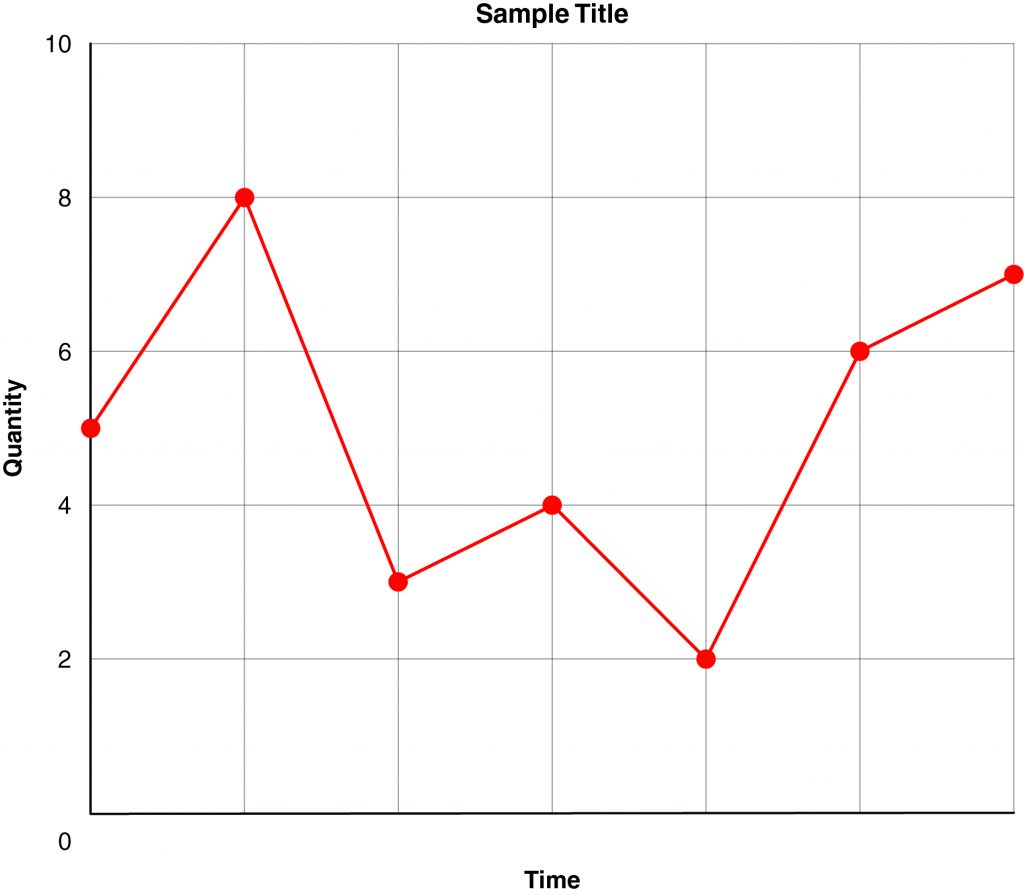
Graphs and charts are used to create visual examples of information, and it is important to be able to interpret them. The examples from Section 1 can show a variety of conclusions.

- The minimum value is 2, and the maximum value is 8.
- The largest decrease is between the second and third points.
- The largest increase is between the fifth and sixth points.

Keep In Mind
Read and determine the parts of the graph before answering questions related to the graph.

- Category B is the highest with 8.
- Category E is the lowest with 2.
- There are no categories that are the same.

- Category B is the largest with 22.86%.
- Category E is the smallest with 5.71%.
- All of the categories are less than one-fourth of the graph.
Try these ATI TEAS math practice questions
Interpreting and Evaluating Line, Bar, and Circle Graphs Review
TEAS Test – Mean, Median, Mode, and Range
The mean, median, mode, and range are common values related to data sets. These values can be calculated using the data set 2, 4, 7, 6, 8, 5, 6, and 3.
The mean is the sum of all numbers in a data set divided by the number of elements in the set. The sum of items in the data set is 41. Divide the value of 41 by the 8 items in the set. The mean is 5.125.
The median is the middle number of a data set when written in order. If there are an odd number of items, the median is the middle number. If there are an even number of items, the median is the mean of the middle two numbers. The numbers in order are 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8. The middle two numbers are 5 and 6. The mean of the two middle numbers is 5.5, which is the median.
Keep In Mind

The mean, median, mode, and range can have the same values, depending on the data set.
The mode is the number or numbers that occur most often. There can be no modes, one mode, or many modes. In the data set, the number 6 appears twice, making 6 the mode.
The range is the difference between the highest and lowest values in a data set. The highest value is 8 and the lowest value is 2, for a range of 6.
Try these TEAS math practice questions
Mean, Median, Mode, and Range Review
Let’s Review!
- A bar graph, line graph, and circle graph are different ways to summarize and represent data.
- The mean, median, mode, and range are values that can be used to interpret the meaning of a set of numbers.
You have covered a lot of math on the TEAS test so far and it’s almost done! In the next lesson we will discuss similarity, right triangles and trigonometry.
You May Subscribe to the online course to gain access to the full lesson content.
If your not ready for a subscription yet, be sure to check out our free practice tests and sample lesson at this link
