The Twentieth Century and Beyond
The Cold War, Part 1
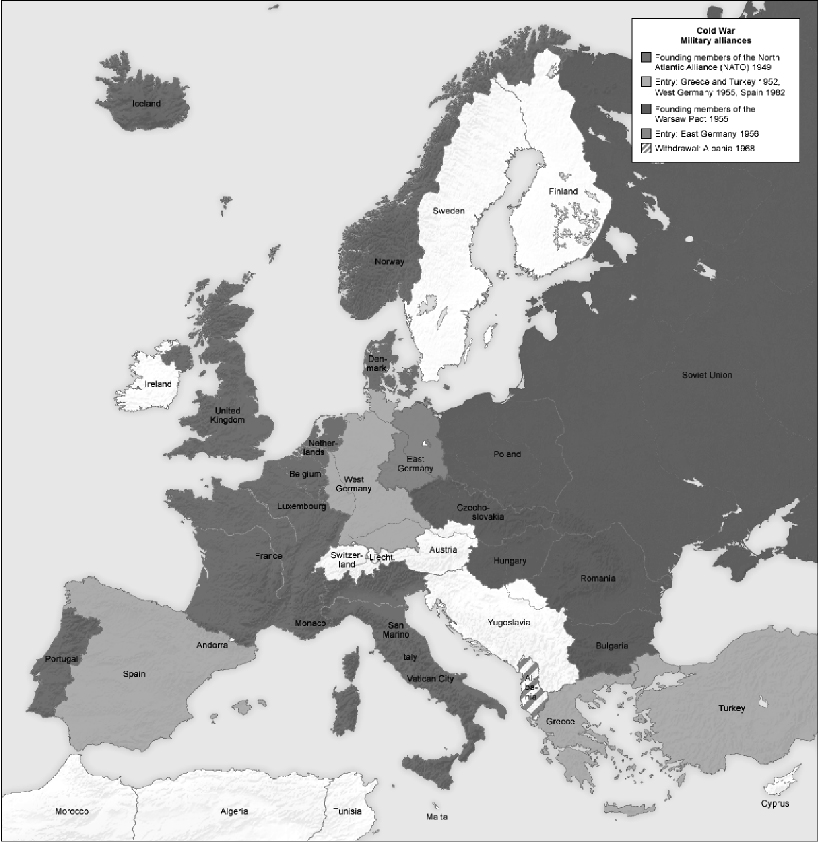
The end of World War II did not resolve all international tensions. After the war, the United States and the Soviet Union struggled to dominate world affairs in a fight called the Cold War. The Soviet Union’s communist ideology threatened many in the United States, and Soviet leaders in turn were afraid of the United States. Both countries began jockeying for power in Europe and around the world, beginning with the division between a capitalist Western Europe and a communist Eastern Europe.
The United States embraced a policy of containment, hoping that confining communism to countries in which it already existed would lead to its reform or collapse. In Europe, this meant supporting reconstruction financially through the Marshall Plan in 1947 and committing to a regional defense pact called the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) in 1949. It became U.S. policy to send aid to countries that were resisting communist aggression in some way, first articulated through the Truman Doctrine.
KEY POINT!
Containment became the basis for U.S. foreign policy for the next 40 years, with minor revisions.

In Korea, which had been divided into a communist north and a U.S.-aligned south, war broke out in 1950, and the United States fought in the Korean War from 1950 to 1953. This war ended in a stalemate. Both the Soviet Union and the United States offered both evelopment aid and military aid to countries that were gaining independence, a practice that fueled conflict around the world. After creating and supporting an independent South Vietnam for some time, the United States became engaged in a protracted war called the Vietnam War that ended with South Vietnam’s defeat in 1975.
Both the United States and the Soviet Union researched and developed nuclear weapons as a deterrent against the other. The United States had used the first atomic bomb against Japan to force its surrender in 1945, but the weapon took on a new significance during the Cold War. The Soviet Union tested its first atomic bomb in 1949, and both the United States and the Soviet Union tested hydrogen bombs in the 1950s. Soon, their arsenals grew to include thousands of these weapons, enough to destroy each other several times over, and the strategy of Mutually Assured Destruction ensured that both sides, if they attacked, would be annihilated.
Example
Which coutry was the rival of the United States during the Cold War?
A. France
B. Germany
C. Great Britain
D. The Soviet Union
The correct answer is D. The United States fought the Cold War against the Soviet Union.
Subscribe to the online course to gain access to the full lesson content.
If your not ready for a subscription yet, be sure to check out our free practice tests and sample lesson at this link
