Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
Cell Respiration
Once cells have been made, they need to be powered. Plants and some other cells can capture the energy of light and convert it into stored energy in ATP. However, most prokaryotic cells and all eukaryotic cells can perform a metabolic process called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the process by which the mitochondria of a cell break down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP. The following is the general equation for cellular respiration:
Reactions during cellular respiration occur in the following sequence:
- Glycolysis: One molecule of glucose breaks down into two smaller sugar molecules called pyruvate. This is an anaerobic process, which means it does not need oxygen to be present. Glycolysis takes place in the cell’s cytoplasm. End product yield from this reaction per one glucose molecule is:
- two molecules of ATP
- two molecules of pyruvate
- two molecules of NADH
- Oxidation of pyruvate: Pyruvate is converted into acetyl coA in the mitochondrial matrix. This transition reaction must happen for pyruvate to enter the next phase of cellular respiration. Pyruvate is oxidized, which means it loses two electrons and a hydrogen molecule. This results in the formation of NADH and loss of CO2.
- Citric acid cycle: Also called the Krebs cycle, during this cycle an acetyl group detaches from the coenzyme A in the acetyl coA molecule. This process is aerobic, which means it must occur in the presence of oxygen. The net yield per one glucose molecule is:
- two molecules of ATP
- six molecules of NADH
- two molecules of FADH2
- four molecules of CO2
- Electron transport chain: This process happens in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It consists of a series of enzymatic reactions. Both NADH and FADH2 molecules are passed through a series of enzymes so that electrons and protons can be released from them. During this process, energy is released and used to fuel chemiosmosis. During chemiosmosis, protons are transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane to the outer mitochondrial compartment. This flow of protons drives the process of ATP synthesis. This step of cellular respiration creates an approximate net yield of 34 ATP per glucose molecule. Six molecules of water are also formed at the end of the electron transport chain.
Keep In Mind

Cellular respiration requires oxygen, but there are forms of fermentation that extract energy from food without using oxygen. Fermentation can be either alcoholic (makes ethanol as an end product, like yeast in the brewing of beer) or lactic acid type. Lactic acid is produced in a person’s muscles during strenuous activity when the body cannot move enough oxygen to the cells.
Did You Know?

The citric acid cycle is not identical for all organisms. Plants have some differences in terms of the enzymes used and energy carriers produced.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process plants use to make a food source from energy. This process can be thought of as the reverse of cellular respiration. Instead of glucose being broken down into carbon dioxide to create energy-containing molecules, energy is captured from the sun and used to turn carbon dioxide into glucose (and other organic chemicals the plant needs). The energy source is the sun. The reaction for photosynthesis is shown below:
CO2 + H2O → C6H12O6 + O2
Energy is captured from the sun and used to turn carbon dioxide into glucose (and other organic chemicals). Chloroplasts are organelles in plants that contain green chlorophyll, which helps the plants absorb light from the sun.
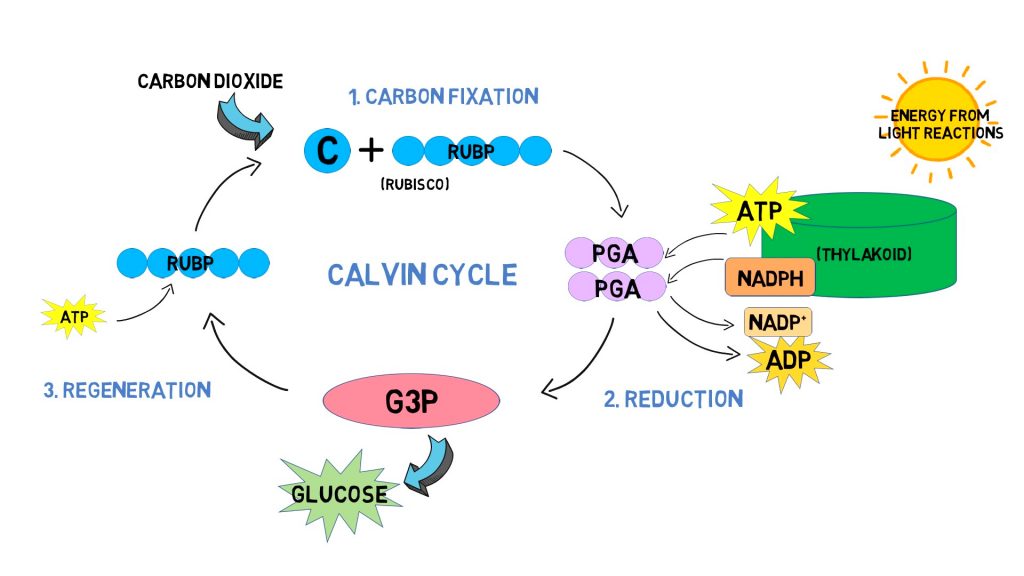
The photosynthetic reaction involves two distinct phases: light reactions and dark reactions. Light-dependent reactions require light to produce ATP and NADPH. During dark reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, light is not required. These reactions use ATP and NAPDH to produce sugar molecules like glucose.
Let’s Review
- Cells are powered by cellular respiration and/or photosynthesis.
- Cellular respiration is the process where mitochondria of a cell break down glucose (sugar molecules) to produce energy in the form of ATP. The general equation for cellular respiration is: O2 + C6H12O6 → CO2 + H2O + ATP
- Reactions during cellular respiration go from glycolysis to the citric acid cycle to the electron transport chain.
- Photosynthesis is the process plants use to make a food source from energy. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, which helps plants absorb light from the sun.
- Photosynthesis is considered the reverse of cellular respiration. The general equation is: (ATP) + CO2 + H2O → C6H12O6 + O2
- The reaction involves two distinct phases: light reactions and dark reactions. Light-dependent reactions require light to produce ATP and NADPH. The dark reactions, also known as the Calvin Cycle, do not require light and use ATP and NADPH from the light reactions to produce glucose and oxygen.

Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Flashcards
You May Subscribe to the online course to gain access to the full lesson content.
If your not ready for a subscription yet, be sure to check out our free practice tests and sample lesson at this link
